[logseq-plugin-git:commit] 2025-12-11T14:50:38.767Z
This commit is contained in:
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
page-title: \"Automatic Backups for WSL2 – Stephen's Thoughts\"
|
||||
url: https://stephenreescarter.net/automatic-backups-for-wsl2/
|
||||
date: \"2023-03-13 15:12:29\"
|
||||
---
|
||||
[Windows Subsystem for Linux](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl) (WSL) is pure awesome, and [WSL2](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl2-index) is even more awesome. (If you’ve never heard of it before, it’s Linux running inside Windows 10 – not as a virtual machine or emulator, but as a fully supported environment that shares the machine.) I’ve been testing WSL2 for a few months now as my local development environment. The performance benefits alone make it worth it. However, there is one problem with WSL2: **there isn’t a trivial way to do automatic backups.**
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will explain the difference between WSL1 and WSL2, and how you can set up automatic backups of WSL2. This is the setup I use to backup all of my WSL2 instances, and it integrates nicely with an offsite backup tool like Backblaze, to ensure I never lose an important file.
|
||||
|
||||
- The Difference Between WSL1 and WSL2
|
||||
|
||||
Under WSL1, the Linux filesystem is stored as plain files within the Windows 10 filesystem. As an example, this is the path for my Pengwin WSL1 filesystem:
|
||||
|
||||
Inside that directly you’ll find the usual Linux directories, such as `etc`, `home`, `root`, etc. This makes backing up WSL2 trivial. Your existing backup program can read the files in this directory and back them up when they change. It’s super simple and *just works*.
|
||||
|
||||
*Important: **Do not modify the files in this directory, ever.** This can corrupt your WSL1 instance and lose your files. If you need to restore files from your backup, restore into a separate directory and manually restore back into WSL1 via other methods.*
|
||||
|
||||
However, under WSL2 the Linux filesystem is wrapped up in a virtual hard disk (`VHDX`) file:
|
||||
|
||||
Using a virtual hard disk in this way greatly enhances the file IO performance of WSL2, but it does mean you cannot access the files directly. Instead you have a single file, and in the case of my Pengwin install, it’s over 15GB! ([If you’re not careful, it’ll grow huge](https://stephenreescarter.net/how-to-shrink-a-wsl2-virtual-disk/)!)
|
||||
|
||||
As such, unlike the trivial backups we get for WSL1, we cannot use the same trick for WSL2. Many backup tools explicitly ignore virtual disk files, and those that do try to back it up will have trouble tracking changes. It may also be in a locked/changing state when a backup snapshot tries to read it… ultimately, it’s just not going to end well.
|
||||
- My WSL2 Backup Solution
|
||||
|
||||
My first idea for backing up WSL2 was to `rsync` my home directory onto Windows. It turns out this approach works really well!
|
||||
|
||||
I use a command like this:
|
||||
|
||||
The above command is wrapped this inside `~/backup.sh`, which makes it easy to call on demand – without needing to get the parameters and paths right each time. Additionally, I added some database backup logic, since I want my development databases backed up too. You’ll find my full `~/backup.sh` script (with other features) at the end of this post.
|
||||
|
||||
This method works incredibly well for getting the files into Windows where my backup program can see them and back them up properly. **However, it is also a manual process.**
|
||||
|
||||
Some users have suggested using cron within WSL2 to trigger periodic backups, however the cron still relies on WSL2 to be running. As a result, you’ll only have backups if your WSL2 is up when your backup schedule is configured to run. That means cron isn’t the most reliable solution. As an aside, I have also seen reports that cron doesn’t always run in WSL. Note, I haven’t tested this myself, so I don’t know the details (i.e. use at your own risk).
|
||||
- Automating WSL2 Backups
|
||||
|
||||
After some creative searching, I discovered the **Windows Task Scheduler**. It’s the equivalent to *cron/crontab* on Linux, and allows you to schedule tasks under Windows. I had no idea such a thing existed, although, in hindsight, it seems pretty logical that it would. Using the *Task Scheduler*, we can set up automatic backups for WSL2.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find it by searching for *Task Scheduler* in the start menu, or by looking in the *Windows Administrative Tools* folder.
|
||||
|
||||
Once it opens, you’ll see something that looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
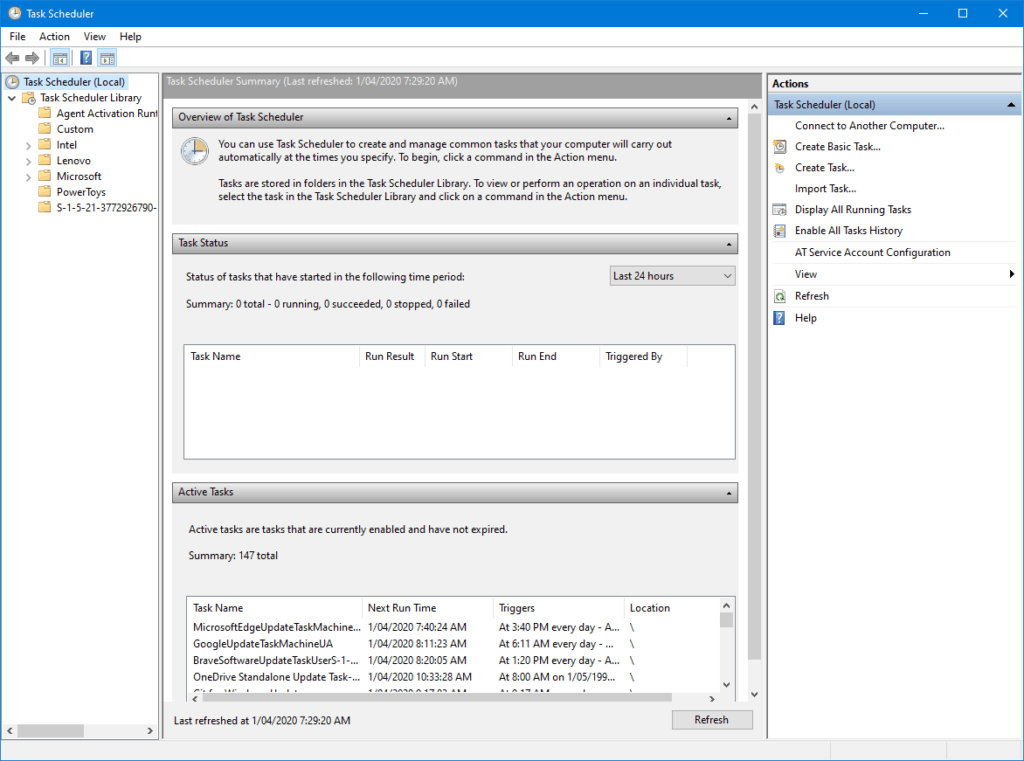
|
||||
|
||||
Windows Task Scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
With the Task Scheduler, we can tie our manual `rsync` based backup up to a schedule.
|
||||
|
||||
To set up our automated backup, I’d recommend first going into the *Custom* folder in the left folder pane. It’ll keep your tasks organised and separate from the system tasks. From there you can select *Create Task…* in the actions list on the right.
|
||||
|
||||
The following screenshots show the configuration I use for my backups, customise as suits your needs. I’ll point out the settings that are important to get it working.
|
||||
|
||||
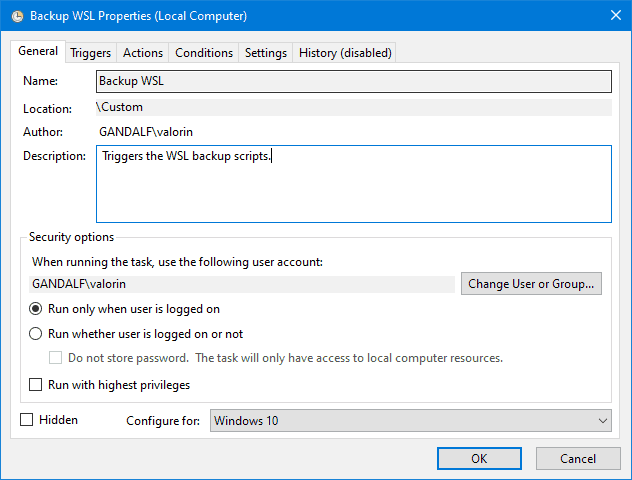
|
||||
|
||||
Set *Configure For* to: `Windows 10`
|
||||
|
||||
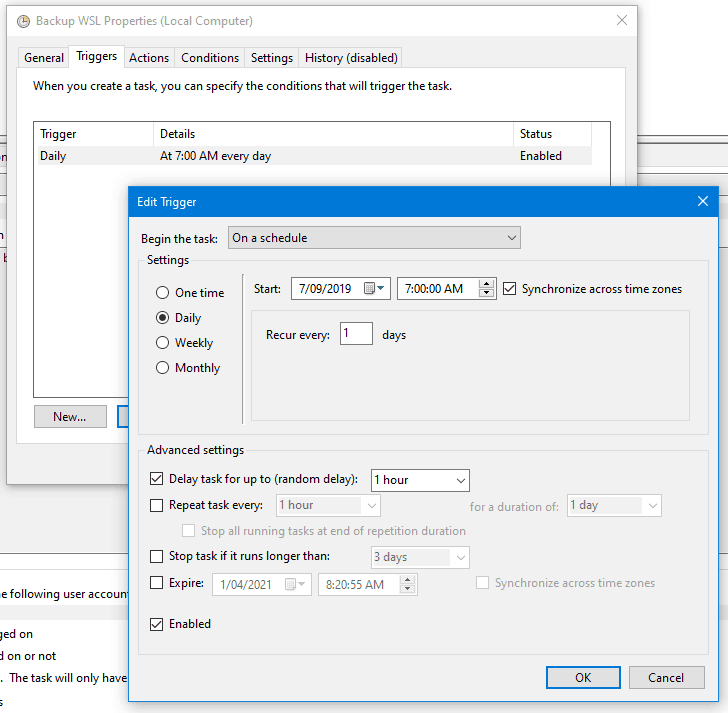
|
||||
|
||||
Click `New` to create a new trigger, which will launch the backup. I have mine configured to run *daily* on a *schedule*, starting at at *random time* between *7am and 8am*. Don’t forget to check *Enabled* is ticked.
|
||||
|
||||
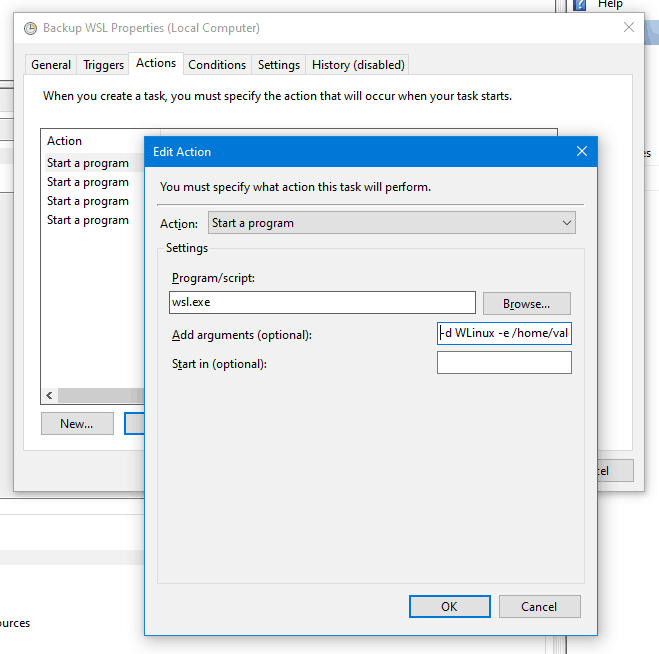
|
||||
|
||||
Click `New` to create a new action, which is how the backup script is executed.
|
||||
|
||||
Set *Program/script* to `wsl.exe`
|
||||
Set *Add arguments* to `-d WLinux -e /home/valorin/backup.sh`
|
||||
|
||||
This executes WSL with the distribution `WLinux` (Pengwin), executing the script `/home/valorin/backup.sh`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
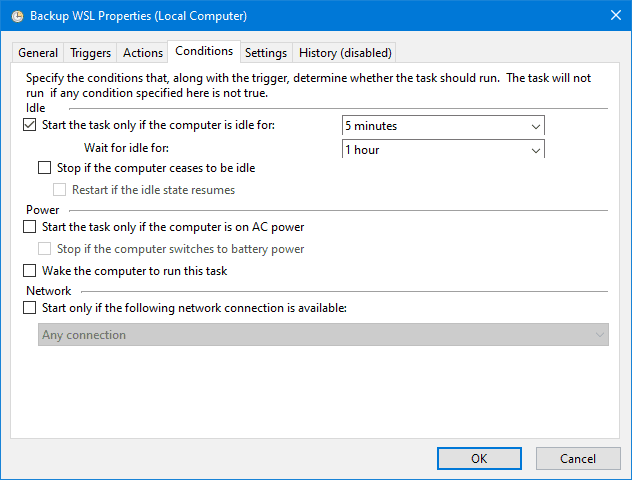
You can control the special conditions when the backup script runs in this tab. Mine waits for the computer to be idle, but it is a laptop and the backup can sometimes slow everything down if there are some large files being backed up.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
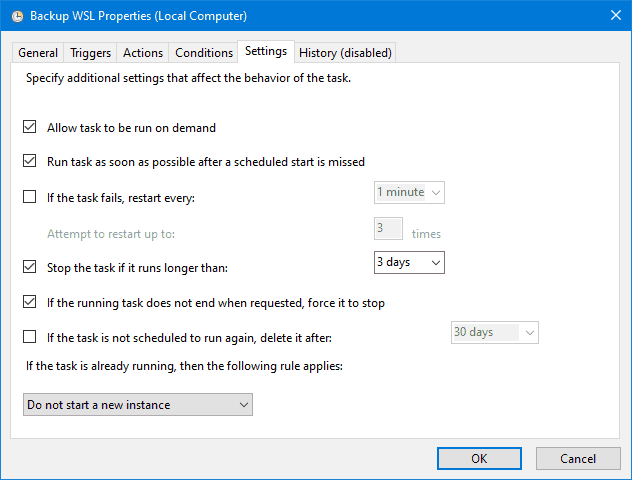
You can configure the settings however suits you best.
|
||||
|
||||
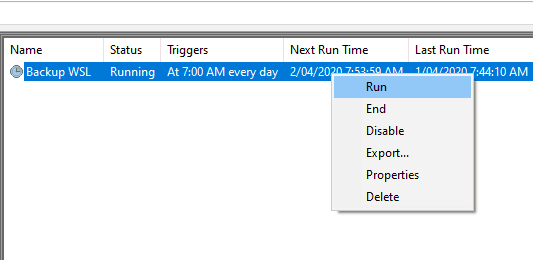
That’s it, you now have automatic backups of WSL2. With the task fully configured, you should be able to wait for the schedule to run at the configured time. You can also right click on the task in the list and select `Run` to manually trigger the backup to check it works.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Backing Up MySQL/MariaDB
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any databases (such as MySQL/MariaDB), you’ll probably want to keep a backup of that data as well. While you could get `rsync` to include the raw database files, that can easily result in corrupted data. So the alternative is to use a tool like `mysqldump` to dump the database data into a file. Once it’s in a file, you can easily include this in the `rsync` backup.
|
||||
|
||||
For my daily backups, I use `mysqldump` to dump all of my current databases into their own files within my home directory. These files are then backed up by `rsync`into Windows alongside everything else. I’ve wrapped all of this up inside `~/backup.sh` , which I keep synchronised between my WSL2 instances.
|
||||
- My `~/backup.sh` Script
|
||||
|
||||
This is the current version of my `~/backup.sh` script. It includes `mysqldump` for my development databases and `rsync` for my files. Since I use it across all my WSL instances, it uses the `WSL_DISTRO_NAME` environment variable to work across all of my WSL instances automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
*Note, you’ll need to allow `sudo mysql` to work without a password to automate the script.*
|
||||
- Summary
|
||||
|
||||
I’ve been using this backup method of automatic backups for WSL2 since I migrated over from WSL1 last year. It works really well with my workflow, and I usually don’t notice the backup window popping up every morning. It’s simple and minimal fuss, and doesn’t require any system changes to WSL2.
|
||||
|
||||
If you do any work or keep any important files within your WSL2, you’ll want to ensure it’s backed up. Coupled with Backblaze, I have WSL2 backed up locally and online, keeping my dev work safe.
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this has been helpful – please reach out if you have any questions about my approach. If you have a different approach to backing up WSL2, please share – I’d love to see how you solve it.
|
||||
@@ -1,129 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Configuring Consul DNS Forwarding in Ubuntu 16.04
|
||||
updated: 2021-09-01 13:45:43Z
|
||||
created: 2021-09-01 13:45:43Z
|
||||
source: https://andydote.co.uk/2019/05/29/consul-dns-forwarding/
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
- DEPRECATED - This doesn’t work properly
|
||||
|
||||
[Please see this post for an updated version which works!](https://andydote.co.uk/2019/09/24/consul-ubuntu-dns-revisited/)
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
One of the advantages of using [Consul](https://www.consul.io/) for service discovery is that besides an HTTP API, you can also query it by DNS.
|
||||
|
||||
The DNS server is listening on port `8600` by default, and you can query both A records or SRV records from it. [SRV](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SRV_record) records are useful as they contain additional properties (`priority`, `weight` and `port`), and you can get multiple records back from a single query, letting you do load balancing client side:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ dig @localhost -p 8600 consul.service.consul SRV +short
|
||||
|
||||
1 10 8300 vagrant1.node.dc1.consul.
|
||||
1 14 8300 vagrant2.node.dc1.consul.
|
||||
2 100 8300 vagrant3.node.dc1.consul.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A Records are also useful, as it means we should be able to treat services registered to Consul like any other domain - but it doesn’t work:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl http://consul.service.consul:8500
|
||||
curl: (6) Could not resolve host: consul.service.consul
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for this is that the system’s built-in DNS resolver doesn’t know how to query Consul. We can, however, configure it to forward any `*.consul` requests to Consul.
|
||||
- [](#solution---forward-dns-queries-to-consul)Solution - Forward DNS queries to Consul
|
||||
|
||||
As I usually target Ubuntu based machines, this means configuring `systemd-resolved` to forward to Consul. However, we want to keep Consul listening on it’s default port (`8600`), and `systemd-resolved` can only forward requests to port `53`, so we need also to configure `iptables` to redirect the requests.
|
||||
|
||||
The steps are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Configure `systemd-resolved` to forward `.consul` TLD queries to the local consul agent
|
||||
2. Configure `iptables` to redirect `53` to `8600`
|
||||
|
||||
So let’s get to it!
|
||||
- [](#1-make-iptables-persistent)1\. Make iptables persistent
|
||||
|
||||
IPTables configuration changes don’t persist through reboots, so the easiest way to solve this is with the `iptables-persistent` package.
|
||||
|
||||
Typically I am scripting machines (using \[Packer\] or \[Vagrant\]), so I configure the install to be non-interactive:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
echo iptables-persistent iptables-persistent/autosave_v4 boolean false | sudo debconf-set-selections
|
||||
echo iptables-persistent iptables-persistent/autosave_v6 boolean false | sudo debconf-set-selections
|
||||
|
||||
sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt install -yq iptables-persistent
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [](#2-update-systemd-resolved)2\. Update Systemd-Resolved
|
||||
|
||||
The file to change is `/etc/systemd/resolved.conf`. By default it looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[Resolve]
|
||||
#DNS=
|
||||
#FallbackDNS=8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 2001:4860:4860::8888 2001:4860:4860::8844
|
||||
#Domains=
|
||||
#LLMNR=yes
|
||||
#DNSSEC=no
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We need to change the `DNS` and `Domains` lines - either editing the file by hand, or scripting a replacement with `sed`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo sed -i 's/#DNS=/DNS=127.0.0.1/g; s/#Domains=/Domains=~consul/g' /etc/systemd/resolved.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The result of which is the file now reading like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[Resolve]
|
||||
DNS=127.0.0.1
|
||||
#FallbackDNS=8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 2001:4860:4860::8888 2001:4860:4860::8844 Domains=~consul
|
||||
#LLMNR=yes
|
||||
#DNSSEC=no
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By specifying the `Domains` as `~consul`, we are telling resolvd to forward requests for the `consul` TLD to the server specified in the `DNS` line.
|
||||
- [](#3-configure-resolvconf-too)3\. Configure Resolvconf too
|
||||
|
||||
For compatibility with some applications (e.g. `curl` and `ping`), we also need to update `/etc/resolv.conf` to specify our local nameserver. You do this **not** by editing the file directly!
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, we need to add `nameserver 127.0.0.1` to `/etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head`. Again, I will script this, and as we need `sudo` to write to the file, the easiest way is to use `tee` to append the line and then run `resolvconf -u` to apply the change:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
echo "nameserver 127.0.0.1" | sudo tee --append /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head
|
||||
sudo resolvconf -u
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [](#configure-iptables)Configure iptables
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we need to configure iptables so that when `systemd-resolved` sends a DNS query to localhost on port `53`, it gets redirected to port `8600`. We’ll do this for both TCP and UDP requests, and then use `netfilter-persistent` to make the rules persistent:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -d localhost -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8600
|
||||
sudo iptables -t nat -A OUTPUT -d localhost -p tcp -m tcp --dport 53 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8600
|
||||
|
||||
sudo netfilter-persistent save
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [](#verification)Verification
|
||||
|
||||
First, we can test that both Consul and Systemd-Resolved return an address for a consul service:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ dig @localhost -p 8600 consul.service.consul +short
|
||||
10.0.2.15
|
||||
|
||||
$ dig @localhost consul.service.consul +short
|
||||
10.0.2.15
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And now we can try using `curl` to verify that we can resolve consul domains and normal domains still:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://consul.service.consul:8500/ui/
|
||||
200
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}\n" http://google.com
|
||||
301
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [](#end)End
|
||||
|
||||
There are also guides available on how to do this on [Hashicorp’s website](https://learn.hashicorp.com/consul/security-networking/forwarding), covering other DNS resolvers too (such as BIND, Dnsmasq, Unbound).
|
||||
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: DotFiles
|
||||
updated: 2021-08-04 14:37:25Z
|
||||
created: 2020-08-19 11:26:42Z
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
[https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/dotfiles](https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/dotfiles)
|
||||
install git and git-lfs
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
apt install git git-lfs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
setup the directory and alias
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git init --bare $HOME/.cfg
|
||||
alias config='/usr/bin/git --git-dir=$HOME/.cfg/ --work-tree=$HOME'
|
||||
config config --local status.showUntrackedFiles no
|
||||
echo \"alias config='/usr/bin/git --git-dir=$HOME/.cfg/ --work-tree=$HOME'\" >> $HOME/.bashrc
|
||||
``````
|
||||
|
||||
example of loading stuff into the repo
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
config status
|
||||
config add .vimrc
|
||||
config commit -m \"Add vimrc\"
|
||||
config add .bashrc
|
||||
config commit -m \"Add bashrc\"
|
||||
config push
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
init a new machine with the repo
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
alias config='/usr/bin/git --git-dir=$HOME/.cfg/ --work-tree=$HOME'
|
||||
echo \".cfg\" >> .gitignore
|
||||
git clone --bare git@github.com:sstent/dotfiles.git $HOME/.cfg
|
||||
config checkout
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Fix WSL to Hyperv network
|
||||
updated: 2023-02-08 17:09:10Z
|
||||
created: 2023-02-08 17:08:43Z
|
||||
latitude: 39.18360820
|
||||
longitude: -96.57166940
|
||||
altitude: 0.0000
|
||||
---
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
Get-NetIPInterface | where {$_.InterfaceAlias -eq 'vEthernet (WSL)'} | Select-Object ifIndex,InterfaceAlias,ConnectionState,Forwarding
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
`Get-NetIPInterface | where {$_.InterfaceAlias -eq 'vEthernet (WSL)' -or $_.InterfaceAlias -eq 'vEthernet (Default Switch)'} | Set-NetIPInterface -Forwarding Enabled -Verbose`
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: How to Shrink a WSL2 Virtual Disk – SCRIPT
|
||||
updated: 2022-10-17 18:47:57Z
|
||||
created: 2022-10-17 18:47:57Z
|
||||
source: https://stephenreescarter.net/how-to-shrink-a-wsl2-virtual-disk/
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
just put the in the flle scriptname.txt the lines
|
||||
|
||||
```batch
|
||||
wsl.exe –terminate WSLinux
|
||||
wsl –shutdown
|
||||
select vdisk file=%appdata%\\..\\Local\\Local\\Packages\\SomeWSLVendorName\\LocalState\\ext4.vhdx
|
||||
compact vdisk
|
||||
exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a task in task scheduler with this action
|
||||
|
||||
`diskpart /s PathToScript\\scriptname.txt > logfile.txt`
|
||||
@@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Powershell - create tasks for FFS
|
||||
updated: 2021-03-08 21:09:39Z
|
||||
created: 2021-03-08 21:09:23Z
|
||||
---
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
|
||||
Get-ChildItem -Path c:\\Users\\sstent\\Documents\\*.ffs_batch | foreach {
|
||||
|
||||
echo $_.FullName
|
||||
|
||||
$DelayTimeSpan = New-TimeSpan -Hours 2
|
||||
|
||||
$A = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute \"C:\\Program Files\\FreeFileSync\\FreeFileSync.exe\" -Argument $_.FullName
|
||||
|
||||
$T = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -Daily -At 7am -RandomDelay $DelayTimeSpan
|
||||
|
||||
$P = New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal \"sstent\" -RunLevel Limited -LogonType Interactive
|
||||
|
||||
$S = New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSet
|
||||
|
||||
$D = New-ScheduledTask -Action $A -Principal $P -Trigger $T -Settings $S
|
||||
|
||||
Register-ScheduledTask $_.Name -InputObject $D -TaskPath \"\\sync\\\"
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Poweshell - delete mepty dirs
|
||||
updated: 2022-01-30 16:39:35Z
|
||||
created: 2022-01-30 16:38:59Z
|
||||
latitude: 40.78200000
|
||||
longitude: -73.99530000
|
||||
altitude: 0.0000
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
|
||||
- Set to true to test the script
|
||||
$whatIf = $false
|
||||
- Remove hidden files, like thumbs.db
|
||||
$removeHiddenFiles = $true
|
||||
- Get hidden files or not. Depending on removeHiddenFiles setting
|
||||
$getHiddelFiles = !$removeHiddenFiles
|
||||
- Remove empty directories locally
|
||||
Function Delete-EmptyFolder($path)
|
||||
{
|
||||
- Go through each subfolder,
|
||||
Foreach ($subFolder in Get-ChildItem -Force -Literal $path -Directory)
|
||||
{
|
||||
- Call the function recursively
|
||||
Delete-EmptyFolder -path $subFolder.FullName
|
||||
}
|
||||
- Get all child items
|
||||
$subItems = Get-ChildItem -Force:$getHiddelFiles -LiteralPath $path
|
||||
- If there are no items, then we can delete the folder
|
||||
- Exluce folder: If (($subItems -eq $null) -and (-Not($path.contains("DfsrPrivate"))))
|
||||
If ($subItems -eq $null)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Write-Host "Removing empty folder '${path}'"
|
||||
Remove-Item -Force -Recurse:$removeHiddenFiles -LiteralPath $Path -WhatIf:$whatIf
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
- Run the script
|
||||
Delete-EmptyFolder -path "G:\Old\"```
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Powershell - get last boots
|
||||
updated: 2021-03-24 14:55:35Z
|
||||
created: 2021-03-24 14:55:24Z
|
||||
---
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
|
||||
Get-EventLog -LogName System |? {$_.EventID -in (6005,6006,6008,6009,1074,1076)} | ft TimeGenerated,EventId,Message -AutoSize -wrap
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Recursive Par2 creation
|
||||
updated: 2022-01-30 22:42:55Z
|
||||
created: 2022-01-30 22:42:30Z
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Recursive Par2 creation
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ECHO ON
|
||||
|
||||
SETLOCAL
|
||||
|
||||
REM check input path
|
||||
|
||||
IF \"%~1\"==\"\" GOTO End
|
||||
|
||||
IF NOT EXIST \"%~1\" (
|
||||
|
||||
ECHO The path does not exist.
|
||||
|
||||
GOTO End
|
||||
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
IF NOT \"%~x1\"==\"\" (
|
||||
|
||||
ECHO The path is not folder.
|
||||
|
||||
GOTO End
|
||||
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
REM set options for PAR2 client
|
||||
|
||||
SET par2_path=\"C:\\Users\\stuar\\Downloads\\sstent\\AppData\\Local\\MultiPar\\par2j64.exe\"
|
||||
|
||||
REM recursive search of subfolders
|
||||
|
||||
PUSHD %1
|
||||
|
||||
FOR /D /R %%G IN (*.*) DO CALL :ProcEach \"%%G\"
|
||||
|
||||
POPD
|
||||
|
||||
GOTO End
|
||||
|
||||
REM run PAR2 client
|
||||
|
||||
:ProcEach
|
||||
|
||||
ECHO create for %1
|
||||
|
||||
%par2_path% c /fo /sm2048 /rr5 /rd1 /rf3 /lc+32 \"%~1\\%~n1.par2\" *
|
||||
|
||||
GOTO :EOF
|
||||
|
||||
:End
|
||||
|
||||
ENDLOCAL
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: 'Script: Re Run'
|
||||
updated: 2022-08-15 12:55:30Z
|
||||
created: 2022-08-15 12:55:30Z
|
||||
source: https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=32467957
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
I use this script, saved as \`rerun\`, to automatically re-execute a command whenever a file in the current directory changes:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
while true; do
|
||||
reset;
|
||||
\"$@\";
|
||||
inotifywait -e MODIFY --recursive .
|
||||
done
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you invoke \`rerun make test\` then \`rerun\` will run \`make test\` whenever you save a file in your editor.
|
||||
@@ -1,108 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Single-file scripts that download their dependencies · DBohdan.com
|
||||
updated: 2023-01-15 15:15:30Z
|
||||
created: 2023-01-15 15:15:30Z
|
||||
source: https://dbohdan.com/scripts-with-dependencies
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
An ideal distributable script is fully contained in a single file. It runs on any compatible operating system with an appropriate language runtime. It is plain text, and you can copy and paste it. It does not require mucking about with a package manager, or several, to run. It does not conflict with other scripts’ packages or require managing a [project environment](https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/venv.html) to avoid such conflicts.
|
||||
|
||||
The classic way to get around all of these issues with scripts is to limit yourself to using the scripting language’s standard library. However, programmers writing scripts don’t want to; they want to use libraries that do not come with the language by default. Some scripting languages, runtimes, and environments resolve this conflict by offering a means to download and cache a script’s dependencies with just declarations in the script itself. This page lists such languages, runtimes, and environments. If you know more, [drop me a line](https://dbohdan.com/contact).
|
||||
|
||||
- Contents
|
||||
- [Anything with a Nix package](#anything-with-a-nix-package)
|
||||
- [D](#d)
|
||||
- [Groovy](#groovy)
|
||||
- [JavaScript (Deno)](#javascript-deno)
|
||||
- [Kotlin (kscript)](#kotlin-kscript)
|
||||
- [Racket (Scripty)](#racket-scripty)
|
||||
- [Scala (Ammonite)](#scala-ammonite)
|
||||
- Anything with a Nix package
|
||||
|
||||
The Nix package manager can [act as a `#!` interpreter](https://nixos.org/manual/nix/stable/command-ref/nix-shell.html#use-as-a--interpreter) and start another program with a list of dependencies available to it.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<a id="cb1-1"></a>#! /usr/bin/env nix-shell
|
||||
<a id="cb1-2"></a>#! nix-shell -i python3 -p python3
|
||||
<a id="cb1-3"></a>print("Hello, world!".rjust(20, "-"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
- D
|
||||
|
||||
D’s official package manager DUB supports [single-file packages](https://dub.pm/advanced_usage).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<a id="cb2-1"></a>#! /usr/bin/env dub
|
||||
<a id="cb2-2"></a>/+ dub.sdl:
|
||||
<a id="cb2-3"></a>name "foo"
|
||||
<a id="cb2-4"></a>+/
|
||||
<a id="cb2-5"></a>import std.range : padLeft;
|
||||
<a id="cb2-6"></a>import std.stdio : writeln;
|
||||
<a id="cb2-7"></a>void main() {
|
||||
<a id="cb2-8"></a>writeln(padLeft("Hello, world!", '-', 20));
|
||||
<a id="cb2-9"></a>}
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Groovy
|
||||
|
||||
Groovy comes with an embedded [JAR dependency manager](http://docs.groovy-lang.org/latest/html/documentation/grape.html).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env groovy
|
||||
@Grab(group='org.apache.commons', module='commons-lang3', version='3.12.0')
|
||||
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils
|
||||
println StringUtils.leftPad('Hello, world!', 20, '-')
|
||||
```
|
||||
- JavaScript (Deno)
|
||||
|
||||
[Deno](https://deno.land/) downloads dependencies like a browser. Deno 1.28 and later can also import from NPM packages. Current versions of Deno require you to pass a `run` argument to `deno`. One way to accomplish this from a script is with a form of [“exec magic”](https://wiki.tcl-lang.org/page/exec+magic). Here the magic is modified from a [comment](https://github.com/denoland/deno/issues/929#issuecomment-429004626) by Rafał Pocztarski.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<a id="cb4-1"></a>#! /bin/sh
|
||||
<a id="cb4-2"></a>":" //#; exec /usr/bin/env deno run "$0" "$@"
|
||||
<a id="cb4-3"></a>import leftPad from "npm:left-pad";
|
||||
<a id="cb4-4"></a>console.log(leftPad("Hello, world!", 20, "-"));
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On Linux systems with [recent GNU env(1)](https://coreutils.gnu.narkive.com/e0afmL4P/env-add-s-option-split-string-for-shebang-lines-in-scripts) and on [FreeBSD](https://www.freebsd.org/cgi/man.cgi?env) you can replace the magic with `env -S`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<a id="cb5-1"></a>#! /usr/bin/env -S deno run
|
||||
<a id="cb5-2"></a>import leftPad from "npm:left-pad";
|
||||
<a id="cb5-3"></a>console.log(leftPad("Hello, world!", 20, "-"));
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Kotlin (kscript)
|
||||
|
||||
[kscript](https://github.com/holgerbrandl/kscript) is an unofficial scripting tool for Kotlin that understands several comment-based directives, including one for dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<a id="cb6-1"></a>#! /usr/bin/env kscript
|
||||
<a id="cb6-2"></a>//DEPS org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.12.0
|
||||
<a id="cb6-3"></a>import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils
|
||||
<a id="cb6-4"></a>println(StringUtils.leftPad("Hello, world!", 20, "-"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Racket (Scripty)
|
||||
|
||||
[Scripty](https://docs.racket-lang.org/scripty/) interactively prompts you to install the missing dependencies for a script in any Racket language.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env racket
|
||||
#lang scripty
|
||||
#:dependencies '("base" "typed-racket-lib" "left-pad")
|
||||
------------------------------------------
|
||||
#lang typed/racket/base
|
||||
(require left-pad/typed)
|
||||
(displayln (left-pad "Hello, world!" 20 "-"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Scala (Ammonite)
|
||||
|
||||
The scripting environment in Ammonite lets you [import Ivy dependencies](https://ammonite.io/#IvyDependencies).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<a id="cb8-1"></a>#! /usr/bin/env amm
|
||||
<a id="cb8-2"></a>import $ivy.`org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.12.0`,
|
||||
<a id="cb8-3"></a>org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils
|
||||
<a id="cb8-4"></a>println(StringUtils.leftPad("Hello, world!", 20, "-"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
Tags: [list](https://dbohdan.com/tags#list), [programming](https://dbohdan.com/tags#programming).
|
||||
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
page-title: \"Small ODROID-XU4 (HC1) scripts ($2059139) · Snippets · Snippets · GitLab\"
|
||||
url: https://gitlab.com/-/snippets/2059139
|
||||
date: \"2023-03-13 15:14:55\"
|
||||
---
|
||||
[](https://gitlab.com/-/snippets/2059139/raw/master/Readme.md \"Open raw\")[](https://gitlab.com/-/snippets/2059139/raw/master/Readme.md?inline=false \"Download\")
|
||||
|
||||
- Small ODROID-XU4 (HC1) scripts
|
||||
|
||||
CPU underclocking, CPU clock reset and CPU temperature display.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Reset the XU4 (HC1) CPU clocks to default.
|
||||
|
||||
set -euo pipefail
|
||||
|
||||
# Auto-restart with sudo.
|
||||
if [[ $UID -ne 0 ]]; then
|
||||
sudo -p 'Restarting as root, password: ' bash $0 "$@"
|
||||
exit $?
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
cpufreq-set -c 0 --max 1500000
|
||||
cpufreq-set -c 4 --max 2000000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Monitor the XU4 (HC1) CPU temperature.
|
||||
|
||||
set -euo pipefail
|
||||
|
||||
# thermal_zone2 seems to be the highest most of the time.
|
||||
while [ true ]; do awk '{printf "\r%3.1f°C", $1/1000}' /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone2/temp; sleep 1; done
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Underclock the XU4 (HC1) CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
set -euo pipefail
|
||||
|
||||
# Auto-restart with sudo.
|
||||
if [[ $UID -ne 0 ]]; then
|
||||
sudo -p 'Restarting as root, password: ' bash $0 "$@"
|
||||
exit $?
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
cpufreq-set -c 0 --max 1000000
|
||||
cpufreq-set -c 4 --max 1000000
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- start > type netplwiz
|
||||
- run netplwiz
|
||||
- click "Users must enter a user name and password to use this computer"
|
||||
- tick/untick even if unticked
|
||||
- click apply
|
||||
- local user name will be shown
|
||||
- enter "microsoft.com" password
|
||||
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: choco
|
||||
updated: 2020-08-19 20:24:55Z
|
||||
created: 2020-08-19 12:44:22Z
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
https://chocolatey.org/docs/helpers-install-chocolatey-zip-package
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Chocolatey v0.10.15
|
||||
adobereader 2020.012.20041
|
||||
autohotkey 1.1.33.02
|
||||
autohotkey.install 1.1.33.02
|
||||
calibre 4.22.0
|
||||
camstudio 2.7.316.20161004
|
||||
chocolatey 0.10.15
|
||||
chocolatey-core.extension 1.3.5.1
|
||||
darktable 3.0.2
|
||||
DotNet4.5.2 4.5.2.20140902
|
||||
emacs 26.3.0.20191219
|
||||
filezilla 3.49.1
|
||||
Firefox 79.0.0.20200817
|
||||
git 2.28.0
|
||||
git.install 2.28.0
|
||||
github 3.2.0.20181119
|
||||
github-desktop 2.5.3
|
||||
GoogleChrome 84.0.4147.135
|
||||
greenshot 1.2.10.6
|
||||
gsudo 0.7.0
|
||||
hugin 2019.2.0
|
||||
hugin.install 2019.2.0
|
||||
joplin 1.0.233
|
||||
KB2919355 1.0.20160915
|
||||
KB2919442 1.0.20160915
|
||||
keepass 2.45
|
||||
keepass-keeagent 0.8.1.20180426
|
||||
keepass-keepasshttp 1.8.4.220170629
|
||||
keepass-plugin-keeagent 0.12.0
|
||||
keepass.install 2.45
|
||||
krita 4.3.0
|
||||
mpc-hc 1.7.13.20180702
|
||||
openssh 8.0.0.1
|
||||
putty 0.74
|
||||
putty.portable 0.74
|
||||
rawtherapee 5.8
|
||||
spacemacs 0.200.13
|
||||
sublimetext3 3.2.2
|
||||
SublimeText3.PackageControl 2.0.0.20140915
|
||||
sumatrapdf 3.2
|
||||
sumatrapdf.commandline 3.2
|
||||
sumatrapdf.install 3.2
|
||||
sumatrapdf.portable 3.2
|
||||
tightvnc 2.8.27
|
||||
vcredist2010 10.0.40219.2
|
||||
vcxsrv 1.20.8.1
|
||||
visualstudiocode 1.23.1.20180730
|
||||
vlc 3.0.11
|
||||
voicemeeter 1.0.7.3
|
||||
voicemeeter.install 1.0.7.3
|
||||
vscode 1.48.0
|
||||
vscode.install 1.48.0
|
||||
windirstat 1.1.2.20161210
|
||||
xnviewmp 0.96.5
|
||||
xnviewmp.install 0.96.5
|
||||
youtube-dl 2020.07.28
|
||||
55 packages installed.
|
||||
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: powerpoint VBA - copy comments
|
||||
updated: 2022-06-14 13:38:24Z
|
||||
created: 2022-06-14 13:37:55Z
|
||||
latitude: 40.75891113
|
||||
longitude: -73.97901917
|
||||
altitude: 0.0000
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```vb
|
||||
Sub CopyComments()
|
||||
Dim lFromSlide As Long
|
||||
Dim lToSlide As Long
|
||||
|
||||
lFromSlide = InputBox(\"Copy comments from slide:\", \"SLIDE\")
|
||||
lToSlide = InputBox(\"Copy comments to slide:\", \"SLIDE\")
|
||||
|
||||
Dim oFromSlide As Slide
|
||||
Dim oToSlide As Slide
|
||||
|
||||
Set oFromSlide = ActivePresentation.Slides(lFromSlide)
|
||||
Set oToSlide = ActivePresentation.Slides(lToSlide)
|
||||
|
||||
Dim oSource As Comment
|
||||
Dim oTarget As Comment
|
||||
|
||||
For Each oSource In oFromSlide.Comments
|
||||
|
||||
Set oTarget = _
|
||||
ActivePresentation.Slides(lToSlide).Comments.Add( _
|
||||
oSource.Left, _
|
||||
oSource.Top, _
|
||||
oSource.Author, _
|
||||
oSource.AuthorInitials, _
|
||||
oSource.Text)
|
||||
|
||||
Next oSource
|
||||
|
||||
End Sub
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: update kernel HC1
|
||||
updated: 2021-09-30 00:45:49Z
|
||||
created: 2021-09-22 16:57:09Z
|
||||
latitude: 40.78200000
|
||||
longitude: -73.99530000
|
||||
altitude: 0.0000
|
||||
---
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
grep UUID /media/boot/boot.ini*
|
||||
apt update
|
||||
apt upgrade -V linux-odroid-5422
|
||||
blkid; grep UUID /media/boot/boot.ini*
|
||||
reboot
|
||||
```
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user